
04June
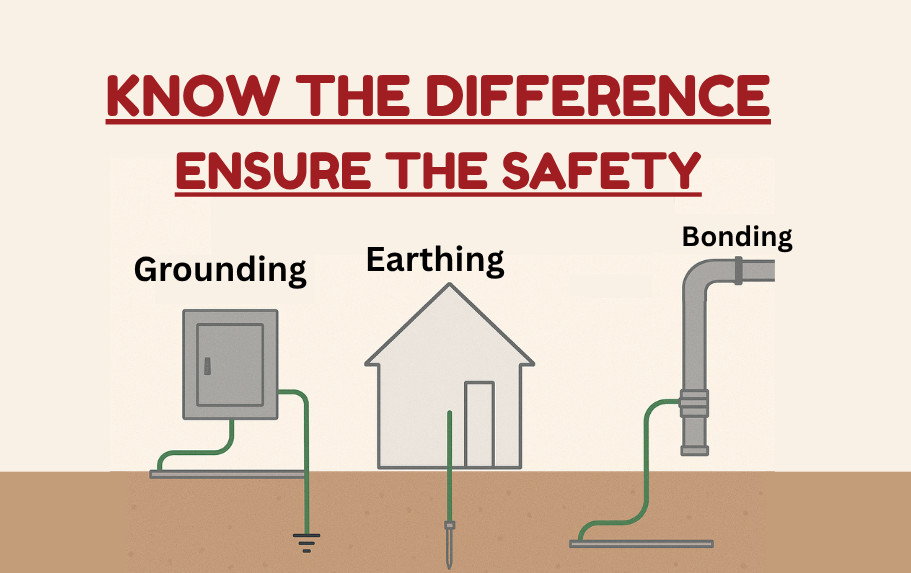
Explore the core differences, applications, and importance of Earthing, Grounding, and Bonding in modern electrical systems.
In order to ensure the safety of electrical circuits there is an alternative path for high and dangerous currents to flow to the Earth so that the problems related to electrical shock and damage to the equipment do not occur. Earthing and grounding are essential concepts in electrical systems that involve connecting electrical equipment and structures to the ground or Earth's surface. The main objective of earthing and grounding is to provide safety, protect against electrical hazards, and ensure proper functioning of electrical systems.
What is Earthing?
Earthing is the process of connecting the non-current carrying parts or the dead parts (metallic parts) of an electrical system to the earth by discharging the electrical energy without any danger. If the earthing is done correctly and if the metallic part comes in contact with the wire, it will be discharged into the earth.
Why Need Earthing?
- Earthing is done to avoid people from getting electric shocks.
- It protects appliances and equipment from getting damaged.
- In case of electrical faults, high voltage passes through electric circuits which damages the electrical installation. If earthing is done, excessive voltage passes through the earth.
- Earthing provides the easiest path to the flow of the short circuit current even after the failure of the insulation.
Example- Earthing the outer metal frame of equipment.
What is Grounding?
Grounding is the process of connecting live parts of an electrical system (through which normally current flows) to the ground or earth. It is very similar to the concept of earthing.
Grounding is used for the protections of equipment and to provide an effective return path from the machine to the power source. Because of surges or lightning, dangerously high current can flow in the electrical distribution system wires. Here grounding allows a safe path for the high current to the ground and minimising the risk to the equipment.
Why Need Grounding?
It is used to balance the unbalanced load and protect the system.
Example- Grounding the neutral of power transformer.
What is Bonding?
Bonding is the process of connecting multiple components that are not intended to carry a current above the ground level. This creates a conductive path between equipment, housing, panels, metal parts and other structures.
In the event of fault or surge, lightning strike or accidental contacts, electricity will flow through the bonded components.so basically bonding distributes an electrical charge.
In order to safeguard the bonded system, they should also be grounded, and this is known as ground bonding.
Why Need Bonding?
It ensures that the bonded components have the same electrical potential at all the time and there cannot be any electrical potential difference anywhere which results in zero current flow.
It is used to trip the circuit breaker when high current flows due to existence/change in the positional difference.
Example- A busbar provides a common ground bonding point for all equipment inside one electrical system.
Relevant Standard referring to Earthing, Grounding and Bonding:
- Grounding is the commonly used word for earthing in the North American (US) & Canadian standards like, NEC, CEC, IEEE, ANSI and UL.
- Earthing is used in European, Common wealth countries and Britain (UK) standards like IS and IEC etc while Grounding is a 6tb bng bit different.
- The electrical bonding is the same term used in both NEC & IEC (US & UK) but totally different than grounding and earthing.
Location of Installation
- Connection between the current carrying parts of the system (such as Neutral as a return path for current) to the ground.
- Connection between the metallic body frame and earth plate in the ground through earth continuity conductor & earthing lead.
- Connection between two equipment, wires, pipes etc (which are non-current carrying during normal operation through a conductor.
Types of Earthing
- Pipe Earthing- In pipe earthing, a galvanized steel and copper perforated pipe is vertically driven into the ground, connecting all the electrical conductors to the earth. The depth of pipe in pipe earthing depends on the conditions of the soil. In this method a layer of salt and charcoal is spread all around the pipe in order to enhance conductivity.
- Plate Earthing- In plate earthing, a galvanized iron plate or a copper plate is used to connect all the electrical conductors to the earth. The plate is not placed at a depth more than three meters or ten feet from the ground level. This method is somewhat costly and requires maintenance.
- Strip Earthing- Strip earthing is very much similar to the plate earthing, where instead of plate a strip is being buried horizontally in the ground. This method is suitable for limited space areas.
- Rod Earthing- A copper or a galvanized iron or a copper bonded steel rod is driven into the ground, either manually or with a hammer, until the desired depth is reached in a hole filled with a conductive compound. The electrical circuit's neutral point is connected to this rod.
Types of Grounding
- Solid Grounding: In this method, one conductor of the electrical system (typically the neutral) is connected directly to the earth. It's commonly used in low-voltage distribution systems.
- Resistance Grounding: A resistor is inserted between the neutral of the system and the ground. This method limits the fault current in the event of a ground fault, reducing potential damage.
- Reactance Grounding: Similar to resistance grounding, but instead of a resistor, a reactor (inductor) is used. Reactance grounding provides better fault current limiting characteristics.
Types of Bonding
- Main Bonding: In this type of Bonding, we connect metallic water, gas and oil pipes as well as structural steel work and lightning protection systems to the main earthing terminal; this is called main protective bonding (previously this was called equipotential bonding).
- Supplementary Bonding: Supplementary bonding is the practise of bonding together exposed conductive parts and extraneous conductive parts ensuring a difference in potential under fault conditions doesn’t occur.
Conclusions
In conclusion, earthing, bonding, and grounding are integral aspects of electrical systems, each serving specific purposes in ensuring safety, proper operation, and protection against electrical hazards. They work together to create a safe and reliable electrical environment, reducing the risk of electric shock, fires, and equipment damage. Proper implementation of earthing, bonding, and grounding practices is essential in both residential and industrial settings to meet safety standards and regulatory requirements.












.png)




.png)
.png)
.png)


